Plastic reinforcement, a process of enhancing plastics with materials like carbon black or glass fibers, plays a pivotal role in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
Its applications demand precision, durability, and compliance with stringent standards. The rapid evolution of global environmental policies and industry demands makes staying informed on regulations and certifications more critical than ever.
This article addresses the key standards for 2025 & beyond, serving as a comprehensive reference for companies and manufacturers seeking to align with emerging regulatory, sustainability, and certification requirements.

The Landscape of Plastic Reinforcement in 2025
Why 2025 is a Pivotal Year For Plastic Reinforcement Regulations:
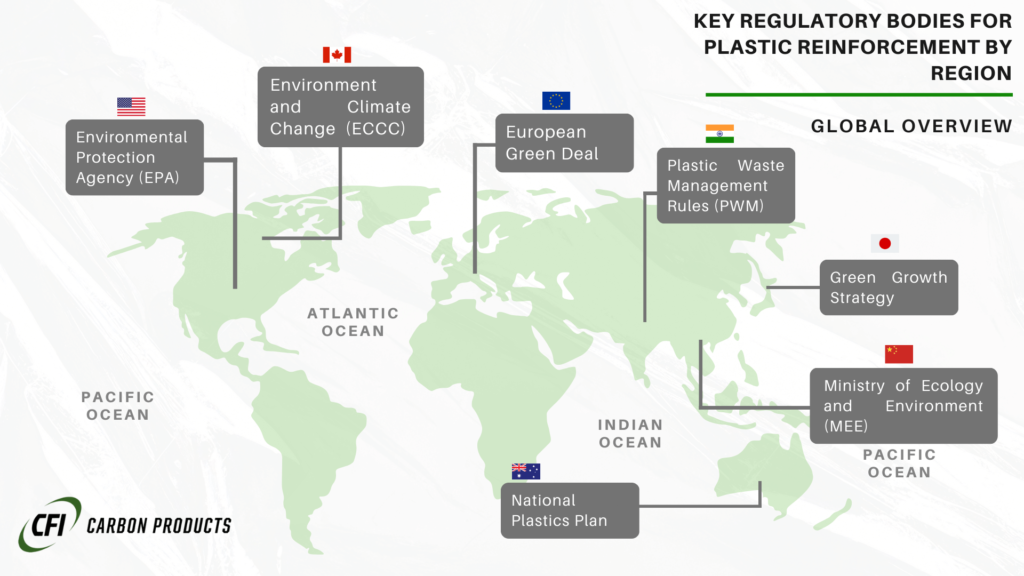
Global environmental initiatives such as the European Union’s Green Deal and the United States’ regulatory updates under the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) have set ambitious targets for reducing emissions and promoting sustainability.
These frameworks emphasize the need for manufacturers to transition toward environmentally friendly practices, particularly in material production and waste management.
In tandem, the rise of consumer awareness and corporate responsibility has led to increased scrutiny of plastic reinforcement materials, urging manufacturers to adopt sustainable and compliant alternatives.
Industries Affected by These Standards
| Industry | Regulatory Impact (2025 & Beyond) |
| Automotive | Stricter emissions standards drive the need for lightweight, high-strength materials. |
| Aerospace | Sustainability mandates push for advanced composite reinforcements with minimal environmental impact. |
| Construction | The adoption of green building certifications requires materials that meet stringent environmental criteria. |
| Packaging | Compliance with circular economy goals necessitates recyclable and biodegradable reinforcements. |
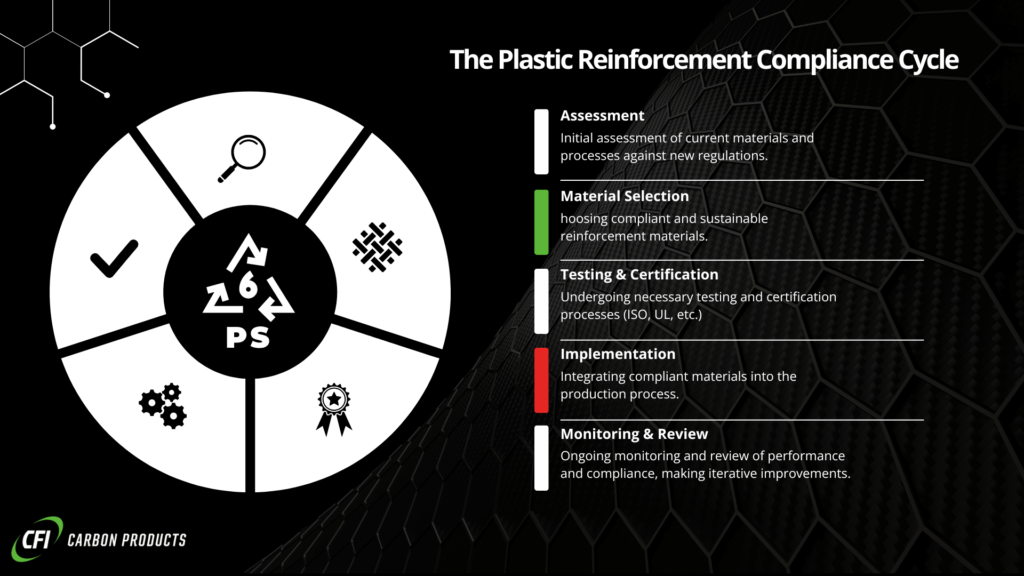
Key Standards and Certifications for Plastic Reinforcement in 2025
Understanding Emerging Standards
2025 marks a significant shift in the regulatory landscape for plastic reinforcement, driven by global sustainability goals and advancements in material science.
Below are some of the pivotal standards and certifications shaping the industry.
Environmental Standards for Plastic Reinforcement
1. ISO 14001: Environmental Management Systems
ISO 14001 continues to be a cornerstone standard for organizations aiming to minimize environmental impact. Its relevance in 2025 is heightened by stricter reporting and compliance requirements, particularly for carbon-intensive industries.
Key Features:
- Framework for establishing environmental policies.
- Focus on continuous improvement of environmental performance.
Applications:
Applicable across industries, including manufacturing plants, where it ensures that environmental considerations are integrated into operational strategies.
| Benefits | Details |
| Compliance | Meets global sustainability goals. |
| Operational Efficiency | Reduces waste and energy consumption. |
| Brand Credibility | Enhances reputation among eco-conscious clients. |
- PDF Version: ISO 14001 Details
2. The European Union’s REACH Regulations
REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals) is critical for ensuring the safe production and use of chemical substances in the EU. For plastic reinforcement, compliance ensures materials avoid hazardous chemicals.
Key Impacts:
- Increased reporting transparency.
- Stringent testing protocols for chemical additives in reinforcements.
| Requirement | Impact on Plastic Reinforcement |
| Chemical Registration | Essential for manufacturers exporting to the EU. |
| Substance Restrictions | Prohibits hazardous additives in reinforced plastics. |
- Full Resource: EU REACH Overview
Product Certification and Safety
3. UL 94: Flammability Testing
UL 94 certification assesses the flammability of plastic materials, crucial for industries like aerospace and automotive, where safety standards are non-negotiable.
Key Criteria:
- Evaluates materials under direct flame exposure.
- Categorizes materials based on flame resistance levels (e.g., V-0, V-1).
Applications in Plastic Reinforcement:
- Reinforced plastics for vehicle interiors and aircraft components require UL 94 compliance to mitigate fire hazards.
| Certification Levels | Description |
| V-0 | Self-extinguishes in 10 seconds. |
| HB | Horizontal burn rate less than 40mm/min. |
- More Information: UL 94 Standard
Sustainability Certifications
4. Cradle-to-Cradle Certification
This standard certifies materials that align with circular economy principles, focusing on the full lifecycle of products from production to recycling.
Certification Levels:
- Bronze: Basic adherence to sustainability criteria.
- Platinum: Comprehensive alignment with eco-design principles.
Applications:
- Reinforced plastics for packaging and construction that are designed for reuse or recycling.
| Criterion | Details |
| Material Health | Avoids toxic or hazardous substances. |
| Circularity | Ensures end-of-life recyclability. |
- Resource: Cradle-to-Cradle Certification
5. Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHGP)
The GHGP standardizes the measurement and management of greenhouse gas emissions, making it critical for manufacturers to report emissions from reinforced plastics.
| Scope | Requirement |
| Scope 1 | Direct emissions from manufacturing processes. |
| Scope 3 | Emissions from the product lifecycle. |
- Resource: GHGP Framework
Benefits:
- Helps organizations identify and mitigate emissions.
- Supports compliance with global climate initiatives like the Paris Agreement.
By adhering to these standards and certifications, manufacturers can not only achieve regulatory compliance but also demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and safety, fostering trust among stakeholders.
Innovations in Plastic Reinforcement Materials for 2025
Pioneering New Materials for Sustainability
The shift toward environmentally friendly and high-performance materials is a driving force behind innovation in plastic reinforcement for 2025.
This section explores cutting-edge advancements, their applications, and how they align with evolving regulations.
Emerging Trends in Reinforcement Materials
1. Carbon Black Alternatives
Carbon black, a common reinforcement agent, is evolving to meet stricter environmental standards. Manufacturers are now exploring low-emission grades and alternative fillers that reduce carbon footprints.
| Innovation | Environmental Benefits |
| Austin Black 325 | Ultra-low PAH content; promotes recyclability. |
| Bio-based Carbon Black | Derived from renewable feedstocks. |
Applications:
- Automotive components like tire reinforcements and interior parts.
- Aerospace materials requiring lightweight, durable composites.
2. Recycled and Bio-based Fibers
With growing regulatory emphasis on circular economy principles, recycled and bio-based fibers are gaining traction as reinforcement materials.
| Fiber Type | Advantages |
| Recycled Glass Fibers | Diverts waste from landfills; reduces resource extraction. |
| Cellulose Fibers | Derived from plants; biodegradable. |
Applications:
- Construction panels and insulation materials.
- Packaging solutions aligned with recyclability goals.
Resource: Circular Economy and Fibers
3. Nanomaterials in Reinforcement
Nanotechnology has unlocked new potential for enhanced mechanical properties in reinforced plastics. Nano-fillers like graphene and carbon nanotubes offer improved strength-to-weight ratios while meeting sustainability goals.
| Nanomaterial | Key Properties |
| Graphene | Exceptional tensile strength; conductive. |
| Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) | High elasticity; lightweight. |
Applications:
- Electronics enclosures requiring EMI shielding.
- High-performance sports equipment.
Advancements in Processing Techniques
1. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
3D printing is revolutionizing the production of reinforced plastics by enabling precise material placement and reducing waste.
Key Benefits:
- Customizable reinforcement designs.
- Efficient use of materials, reducing excess.
| Technique | Impact on Sustainability |
| Fused Deposition Modeling | Minimizes material waste; uses recyclable filaments. |
| Selective Laser Sintering | Enables high-strength, lightweight components. |
2. Hybrid Reinforcement Systems
Hybrid systems combine multiple reinforcement materials, offering tailored properties to meet diverse industry needs.
| Hybrid Material | Key Benefits |
| Carbon Fiber + Glass Fiber | Combines strength and cost-efficiency. |
| Polymer Matrix + Nanofillers | Enhances thermal and mechanical performance. |
Applications:
- Aerospace panels balancing weight and rigidity.
- High-stress automotive components.
Resource: Hybrid Materials Insights
Adopting these innovative materials and processes allows industries to align their operations with the sustainability and performance demands of 2025 & beyond.
Future Outlook for Plastic Reinforcement
Anticipating Industry Shifts Post-2025
As industries adapt to the stringent standards of 2025, the focus will increasingly shift toward long-term innovation, strategic sustainability goals, and deeper integration of technology in materials science.
This section examines future trends that will shape the plastic reinforcement landscape beyond 2025.
Key Drivers for Future Growth
1. Intensified Regulatory Frameworks
Governments worldwide are expected to expand existing policies, pushing industries toward net-zero emissions and stricter waste management practices.
| Projected Regulation | Impact on Reinforcement |
| Global Plastics Treaty Goals | Mandates for recycled content in reinforcement materials. |
| Stricter Waste Disposal Laws | Increased demand for fully recyclable composites. |
Example: The European Union’s expected “Zero Plastic Waste” directive will further restrict single-use and non-recyclable reinforcements.
- For More information: UNEP Global Plastics Treaty
2. Advances in Smart Materials
Smart materials with properties like self-healing and shape memory are set to revolutionize reinforced plastics.
| Feature | Advantage |
| Self-Healing Polymers | Reduces maintenance costs; extends material lifespan. |
| Shape Memory Alloys | Allows structures to adapt to environmental changes. |
Applications:
- Aerospace: Adaptive airframes for fuel efficiency.
- Construction: Dynamic load-bearing structures.
Resource: Smart Materials Innovations
R&D as a Catalyst for Sustainability
1. Collaborative Research Initiatives
Partnerships between industries, academia, and governments are expected to fuel cross-sector innovation in plastic reinforcement.
| Initiative | Goal |
| Horizon Europe Program | Develop sustainable composites for transport. |
| NSF Grants on Polymer Research | Advance recycling-friendly polymer matrices. |
- Resource: Horizon Europe Funding Opportunities
2. AI and Data-Driven Optimization
Artificial intelligence will play a pivotal role in optimizing material selection, reducing waste, and predicting performance under diverse conditions.
| AI Application | Benefit |
| Material Property Prediction | Accelerates R&D cycles for reinforcement materials. |
| Manufacturing Process Control | Reduces defects; enhances efficiency. |
Example: AI-powered platforms like MATLAB are increasingly being used for composite material modeling.
Preparing for the Future of Plastic Reinforcement:
The future of plastic reinforcement will depend on the industry’s ability to:
- Adapt to changing regulations by investing in sustainable and compliant materials.
- Leverage emerging technologies like nanotechnology and AI to drive innovation.
- Collaborate across sectors to align with global sustainability goals.
By embracing these strategies, manufacturers can not only ensure compliance but also gain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
The plastic reinforcement industry stands at a critical juncture in 2025, shaped by stringent environmental regulations, evolving certifications, and the urgent need for sustainability. As a cornerstone material in industries like automotive, aerospace, construction, and packaging, staying ahead of these shifts is essential for long-term viability and competitiveness.
Key Takeaways:
- Understand the 2025 Standards: Familiarize yourself with regulations like ISO 14001 updates and regional laws such as the EU’s Green Deal and EPA mandates.
- Invest in Sustainable Materials: Shift toward environmentally friendly options, such as materials with high recycled content or advanced composites with reduced environmental footprints.
- Leverage Technology: Embrace AI, smart materials, and innovative manufacturing processes to optimize performance and sustainability.
- Collaborate Strategically: Join research initiatives and industry groups to stay ahead of policy changes and innovation trends.
By aligning with these principles, manufacturers can navigate the complexities of 2025 while contributing to a sustainable and efficient future. This proactive approach not only ensures compliance but also builds trust with stakeholders, from regulators to environmentally conscious consumers.


